Clinical Neurophysiology;Journal of Neuroscience Methods:苏州医工所在人脑的疼痛信号研究中取得进展
痛觉既是机体的一种保护机制,亦是困扰很多人的一种病患,但人脑到底是如何产生痛觉以及它又是如何消失的,仍然不甚清楚。
中科院苏州医工所研究员王守岩的神经工程研究组以神经病理性疼痛患者为研究对象,利用独特的深部脑刺激植入研究手段,从人脑感觉丘脑和室周灰质区/导水管周围灰质区(periventricular gray/periaqueductal gray,PVG/PAG)记录场电位信号,以期探索与疼痛缓解密切相关的神经电生理特征。
研究发现丘脑和PVG/PAG脑区中存在多个与疼痛缓解相关的神经波动,包括theta、alpha和beta等多个成分,且这些成分与疼痛缓解存在正、负双向相关关系,表明疼痛调控的多维度特征,其研究结果发表在Clinical Neurophysiology上。
原文链接:
Characteristics of local field potentials correlate with pain relief by deep brain stimulation.
原文摘要:
To investigate the link between neuronal activity recorded from the sensory thalamus and periventricular gray / periaqueductal gray (PVAG) and pain relief by deep brain stimulation,Local field potentials (LFPs) were recorded from the sensory thalamus and PVAG post-operatively from ten patients with neuropathic pain. The LFPs were quantified using spectral and time-frequency analysis, the relationship between the LFPs and pain relief was quantified with nonlinear correlation analysis.
研究人员进而针对疼痛特征的多维建模需求,提出场电位信号神经波动分析的RBC理论,即从神经波动的节律、平衡和耦合神经行为特征,建立三维空间神经活动编码方法,并证明该方法能够刻画不同局部脑网络的复杂活动,成果发表在Journal of Neuroscience Methods上。
原文链接:
Measuring complex behaviors of local oscillatory networks in deep brain local field potentials.
原文摘要:
Multiple oscillations emerging from the same neuronal substrate serve to construct a local oscillatory network. The network usually exhibits complex behaviors of rhythmic, balancing and coupling between the oscillations, and the quantification of these behaviors would provide valuable insight into organization of the local network related to brain states. An integrated approach to quantify rhythmic, balancing and coupling neural behaviors based upon power spectral analysis, power ratio analysis and cross-frequency power coupling analysis was presented. Deep brain local field potentials (LFPs) were recorded from the thalamus of patients with neuropathic pain and dystonic tremor.
这些研究发现与方法将有助于建立疼痛及其治疗的预测模型,为疼痛机制研究、神经调控策略发展提供了理论与技术基础,将推动疼痛治疗深部脑刺激、脊髓刺激等先进神经调控技术发展。
该项研究工作由黄永志博士及其导师王守岩研究员与英国牛津大学John Radcliffe Hospital神经外科合作完成,受到中科院百人计划、江苏省创新人才计划和苏州市神经工程技术重点实验室等项目资助,为神经工程研究组系列工作的一部分(Exp Brain Res 232(2):527-34,2014; Exp Neurology 239(1):248-255, 2013; Neurology 72(6):569-71,2009)。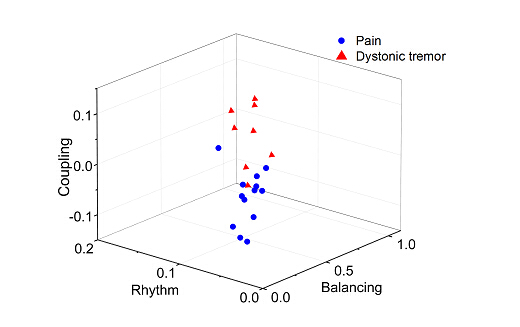
图2:基于RBC理论的三维空间神经波动行为学分析方法在疼痛与肌张力障碍两种疾病神经活动的表现
中科院苏州医工所神经工程研究组专注于人脑深部场电位信号编码分析,交互式智能神经调控技术及机制研究,以及可穿戴医疗设备研发。研制了无线程控光刺激、多感知神经电刺激器、神经生理行为无线监测、微型电化学仪等科研仪器与医疗设备,推动工程技术与临床神经科学交叉融合。
(作者:罗回春,黄永志 )
上一篇:Cell:为实现精准医疗揭示系统性红斑狼疮的分子异质性

